Theme: Recent Scientific Research Approaches and Development in Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectra 2020
Mass Spectra 2020
It's our privilege to invite all the researchers, developers, and experts on behalf of committee members to be the part of the prestigious 8th Global Conference on Mass Spectrometry schedule on March 23-24, 2020 in Osaka, Japan. We aim to unify all the people indulged in this vast field and share the knowledge, explore and look forward to the new way by integrating new thoughts and customizing the limits of future technology.
Mass Spectra 2020 offers a dais to take attention to explore, grip and meet with prominent speakers of the field, including both broad and specific subjects. The Mass Spectra 2020 will be surrounding around the theme “Recent Scientific Research Approaches and Development in Mass Spectrometry”.
The Mass Spectra 2020 is designed with the keynote sessions, session lectures, poster presentations, presentations from the young researchers, Panel Discussions, and the B2B meetings with world-renowned speakers from the stream of Mass Spectrometry. It provides the best platform for the researchers to the researchers all over the globe to introduce themselves to the innovative world with their unique research.
WHY TO ATTEND?
Global Conference on Mass Spectrometry is amid the World's leading technical Conferences. The two days event on Mass Spectrometry will host 60+ Scientific and technical sessions and sub-sessions on leading and latest research transformation related to the field, covering the globe. Mass Spectra Conference 2020 will comprise of 15 major sessions designed to offer comprehensive sessions that discourse current topics in the field.
The attendees can find exclusive sessions and panel discussions on the latest innovations in Mass Spectroscopy by:
-
Lectures from renowned speakers
-
Keynote forums by Prominent Professors, Engineers
-
Open Innovation Challenges
-
Poster presentations by Young Researchers
-
Global Networking sessions with 50+ Countries
-
Novel techniques to benefit your research
-
Best platform for Global business and Networking opportunities
-
Meet the editors of refereed journals, Society and Association members across the Globe
-
Excellent platform to showcase the latest innovation and concept in the technical field
Target Audience:
-
Academicians
-
Scientists
-
Directors of the analytical chemistry department in Universities
-
Research laboratories
-
Professors and Associate professors
-
Graduates and Post Graduates
-
Research scholars
-
Analytical instrument manufacturing companies
-
Research and Development Department.
-
Laboratory ProfessionalsPh.D. Students
Scope and Importance
The Mass Spectrometry community is probably the largest group of scientists working around a single tool. Mass Spectrometry (MS) is arguably the most important analytical spectroscopic tool of modern times. There is no single area of experimental science where Mass Spectrometry is not being used. There is no university or research institution in the developed world without a Mass Spectrometer.
The research service analyzes the global Mass Spectrometry market. The product segments covered include single quadrupole LC-MS, tandem quadrupole LC-MS, GC-MS, TOF LC-MS, ICP-MS, and MALDI-TOF MS. End-user groups have been divided into the academic and government, pharma/biopharmaceuticals, industrial sectors, and applied markets. Revenue forecasts have been provided for product segments and end users from 2012 through 2022. Regionally, the market has been segmented into North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific/Rest of the World. The study also offers distribution channel and competitive analyses, discusses the key market drivers and restraints, and provides prevalent market and technology trends.
Track 1: Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique used to identify the amount and type of chemicals present in a sample by measuring the mass to charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions. Mass spectrometry works by ionizing chemical compounds to produce charged molecules or molecule fragments to measure their mass to charge ratios.
-
Ion Sources
-
Mass Analysers
-
Detectors and Computers
-
Analysis of Biomolecules
Track 2: New Approaches & Recent Advancements in Mass Spectrometry
One of the most exciting and powerful developments in the evolution of mass spectrometry technology is the commercialization of hybrid instruments. Hybrid machines are made by combining two different types of mass analyzers together in tandem; one can now choose almost any combination of quadrupole, TOF, ion trap, or FT ion cyclotron resonance (ICR) hybrid. The hybrid instruments promise the ability to combine the best features from the different components and allow tandem mass spectrometry experiments and unique scanning modes that are not possible on a single instrument.
-
Ion Trap-based MS systems
-
Quadrupole-based MS systems
-
Time of flight-based MS systems
-
Integrated and Hybrid-based MS systems
-
Data Independent Analysis and Hyper Reaction Monitoring
Track 3: Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry, abbreviated MS/MS, is any general method involving at least two stages of mass analysis, either in conjunction with a dissociation processor in a chemical reaction that causes a change in the mass or charge of an ion. The process initiates by isolating a biomolecule of interest from a biological sample and then fragmenting it into multiple subunits in order to help elucidate its composition and sequence. To accomplish this, mass spectrometers are arranged in series. The first spectrometer is arranged to ionize a sample and filter ions of a specific mass to charge ratio. Filtered ions are then fragmented and passed to a second mass spectrometer where the fragments are analyzed.
-
Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Space or in Time
-
Tandem Mass Spectrometry Scan Modes
-
Collision-Activated Decomposition or Collision-Induced Dissociation
-
Reactions Studied in MS/MS
-
Tandem Mass Spectrometry Applications
Track 4: Applications in Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry depicts an important technique with a myriad of various applications in biology, chemistry, and physics, along with clinical medicine and space exploration. Mass ionization spectrometry has become an increasingly important method in the clinical laboratory for the structural study and quantitative measurement of metabolites in a complex biological sample. It is an analytical method with high specificity and a growing presence in laboratory medicine. Several mass spectrometers are being used in a growing number of clinical laboratories and significant improvements in assay performance are rapidly taking place in areas such as toxicology, endocrinology, and biochemical markers. Mass spectrometry is also becoming increasingly used in geologic research for petroleum composition measurement and carbon dating. Thus, mass spectrometry is becoming very prominent in all sorts of clinical and other research endeavours. Thus a basic grip of the technology is necessary to understand all the possible productive interactions.
-
Isotope ratio MS: isotope dating and tracing
-
Trace gas analysis
-
Atom probe
-
Pharmacokinetics
-
Protein characterization
-
Space exploration
-
Respired gas monitor
-
Preparative mass spectrometry
Track 5: Maintenance, Troubleshooting, Data Analysis and Experimentation
Mass spectrometry(MS) is a high-throughput exploratory technique that describes particles by their mass-to-charge proportion. The MS consist of sample preparation, molecular ionization, detection, and instrumentation analysis processes. MS is beneficial as it is generally fast, requires a small amount of sample, and provides high accuracy measurements. The performance of a mass spectrometer will be severely affected by the lack of a good vacuum in the ion transfer region of the mass analyzer. With the deterioration of the vacuum, it will become insufficient to maintain biomedical instrumentation in the operating mode. In case if the foreline pump is not maintained, the oil may become so contaminated that the optimum pumping is no longer possible. Initially, gas transport and metabolism ballasting may refine the oil. On decolorization of the oil, it should be changed according to the pump manufacturers maintenance manual. With the utilization of rotary pumps, to pump away conflict resolution, the solvent may become dissolved in the oil causing an increase in backing line pressure.
-
Data independent analysis, representation, and acquisition
-
Troubleshooting tips and tricks
-
Hyper reaction monitoring
-
Temperature and pressure symptom
-
Air leaks, contamination, error message
Track 6: Configurations and Separation Techniques
Mass spectrometry configurations and techniques are regarded to Mass Spectrometry configuration of source, analyzer, and detector becomes conventional in practice. Various mass spectrometers are being used in a number of clinical laboratories and as a result, significant improvements in assay performance are occurring rapidly in areas such as toxicology, endocrinology, and Biochemical genetics. Atoms of elements vary in masses and thus knowledge of the molecular mass can very often be translated into knowledge of the chemical species involved. Depending on the samples chemical and mechanical properties, different ionization techniques can be used. One of the main factors in choosing which ionization technique to be used is the biochemical process. For samples that are not thermolabile and relatively volatile, ionization such as Electron Impact and/or Chemical Ionization can be effectively used.
-
UV and IR spectroscopy
-
Micro/nanostructured materials
-
Solid phase micro-extraction (SPME)
-
Solid-liquid separations and purification
-
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
-
Design and demonstration of mass spectrometry
-
Instrumentation principles involving mass spectrometry
-
Mini/Portable/Fieldable mass spectrometry
-
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry
-
Proton-extraction-reaction mass spectrometry (PER-MS)
-
Electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry
-
Separation enhancement by electric means
Track 7: Imaging Mass Spectrometry
Imaging Mass Spectrometry is basically a device designed to determine the mass of individual atoms or molecules. It is a technique utilized in mass spectrometry to visualize the spatial arrangement of molecules like metabolites, biomarkers, proteins, peptides, etc. by their molecular masses.
-
Biomolecular imaging mass spectrometry
-
Peptide Imaging Using Mass Spectrometry
-
Quantitative imaging mass spectrometry
Track 8: Ionization techniques
In the ion sources, the analyzed samples are ionized prior to analysis in the mass spectrometer. Many ionization techniques are used for mass spectrometry. The most important considerations are the internal energy transferred during the ionization process and the physicochemical properties of the analyte that can be ionized. Some of the ionization techniques are very energetic and cause extensive fragmentation. Other techniques may be softer and may only produce ions of the molecular species.
-
Gas Phase ionization
-
Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization
-
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization
-
Field desorption and ionization
-
Fast Atom Bombardment
-
Electrospray Ionization
-
Electron Impact Ionization
-
Chemical Ionization
-
Laser & Plasma Desorption
-
Thermospray
-
Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization
-
Inorganic Ionization Sources
Track 9: Mass Spectrometry in Food Analysis
A food matrix is very complex; in addition to major components such as lipids, proteins, and saccharides, a wide range of other natural minor compounds are contained (e.g., vitamins, aroma and flavor compounds, pigments). Under certain conditions, contaminants and other hazardous compounds may be present in food matrices as a consequence of human activities or due processing practices. During recent years, MS techniques have proved to be an excellent tool for qualitative characterization and quantitative determination of various food components because of their high sensitivity and specificity. The determination of organic trace compounds in food analysis is of major importance for food quality and food safety aspects. Both the separation of the analyte from potential inferences in the food matrix, as well as the qualitative and quantitative determination of the target compound, is vital steps in analytical food chemistry.
-
Natural Substances in Food
-
Food Contaminants
-
Processing Contaminants
-
Migrants From Packaging
Track 10: Mass Spectrometry in Forensic Science
Forensic Sciences is the application of a broad spectrum of sciences to answer questions of interest to the legal system. Mass spectrometry has become a valuable tool in forensic science, where it can provide clues from the barest traces left by a suspect. It is used commonly in forensic laboratories for the confirmation of drugs and identification of ignitable liquids.
-
Toxicology Analysis
-
Trace Evidence
-
Arson Investigations
-
Explosive Residue
Track 11: Mass Spectrometry in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an important analytical tool with many applications in pharmaceutical and biomedical field. The increase in sensitivity and resolution of the instrument has uncovered new dimensions in the analysis of pharmaceuticals and compound metabolites of biological systems. Comparing with other techniques, mass spectroscopy is only the technique for molecular weight determination, through which we can predict the molecular formula. It is based on the conversion of the sample into the ionized state, with or without fragmentation which is then identified by their mass-to-charge ratios.
-
Structure elucidation of unknown compounds
-
Quantitative elemental analysis
-
Sensitive detector for chromatographic techniques
-
In vivo studies in humans
Track 12: Mass Spectrometry of Polymers
Recent advances in soft ionization techniques for mass spectrometry of polymeric materials make it possible to determine the mass of intact molecular ions exceeding 1 × 106 Da. Developments in high-resolution mass spectrometers have additionally led to impressive advances in our ability to characterize polymers. The entire molecular mass distribution of a polymer sample can be accurately measured. From the molecular mass, the molecular formulae and information regarding polymer composition and end-groups can be deduced.
-
Pyrolysis
-
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscometry
-
Liquid Chromatography- Mass Spectrometry
-
MALDI
-
Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry
-
Laser desorption mass spectrometry
-
Electrospray ionization
Track 13: Mass Spectrometry in Proteome Research
Mass spectrometry has been commonly used to examine natural examples and has grown into a crucial device for proteomics to look into. Mass spectrometry is an essential system for the exact mass confirmation and depiction of proteins which groups methodologies and instrumentations which are made for its numerous jobs. Its applications connect the conspicuous evidence of proteins and their post-translational changes, the clarification of protein structures, their subunits, and utilitarian collaboration, and what's more the overall estimation of proteins in proteomics. It can be used in a similar manner to limit proteins to the distinctive organelles, and choose the joint efforts between different proteins and furthermore with film lipids.
-
Proteomics
-
Top-down and bottom-up approaches
-
Relative and absolute protein quantitation
Track 14: Mass Spectrometry in Drug Discovery and Drug control
The application of Mass Spectrometry in the pharmaceutical sector linked with the Drug Discovery and Development process is rich and diverse. Many of the initial efforts were connected with online high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in drug metabolism, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. Many innovative efforts to apply various mass spectrometric techniques in early drug discovery, preclinical and clinical development, as well as in Phase 0 studies using Accelerator Mass Spectrometry. Today there is a reevaluation and refocusing on how to efficiently adopt, adapt and use modern Mass Spectrometry instrumentation in the Drug Discovery and Development process.
-
Quantitative Analysis by Mass Spectrometry
-
Mass Spectrometry in Small Molecule Drug Development
-
Future Perspectives in Drug Development
Track 15: Mass spectrometry in environmental analysis
A broad variety of contaminants with the potential to cause harm to humans and animals can make their way into the environment. They may be found in the air, water, and soil and may come from sources such as industrial waste, landfill sites, pesticides, and pharmaceutical drugs. Identification of these contaminants is challenging because of the huge variety of potential compounds with varying chemical compositions. The administration of these components often requires monitoring for the presence of very low concentrations of a variety of contaminants. These challenges call for advanced analytical techniques which are sensitive, robust, fast and cost-effective. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry are two major techniques which can help in detecting environmental contaminants. In the past few decades, developments in both techniques have improved their applicability to environmental analysis.
-
Chromatography in Environmental Analysis
-
Mass Spectrometry in Environmental Analysis
-
Combining LC with MS
Glance at Market Analysis of Mass Spectrometry
The Global Mass Spectrometry Market, mainly driven by means of technological advancements, accelerated pharmaceutical research, developing concern for food safety, and extends in investments, funds, and grants through government bodies worldwide, was valued at $4017 million in 2013, and anticipated to reach $6096 million by 2018, at a CAGR of 8.7%.
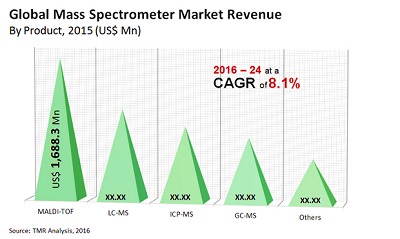
The report ‘Global Mass Spectrometry Market forecast, 2012-2018’ analyzes the market by segments on the basis of technologies, such as tandem LC/MS, LC/MS-TOF, MALDI-TOF, single quadruple, Fourier transform, and gas chromatography. The Mass Spectrometry market is predominantly driven via the tandem LC/MS technology, accompanied by gas chromatography, and LC/MS-TOF. With a market worth of $1687.1 million and $602.6 million, Tandem LC/MS and Gas Chromatography segments have been contributing 42% and 15% respectively to the complete internal beam radiotherapy units market.
Market Value on Pharmaceutical Research:
According to the World Health Organization, The global pharmaceuticals market is worth $300 billion a year, a figure that is expected to rise to $400 billion within three years. The 10 largest drugs companies in this sector have control over one-third of this market, several with the sales of more than $10 billion a year and profit margins of about 30%. Six are based totally in the United States and four in Europe. It is anticipated that North and South America, Europe, and Japan will proceed to account for a full 85% of the global pharmaceuticals market properly into the 21st century.
Market Growth of Mass spectrometry Research in the last and upcoming ten years:
The global mass spectrometry market was valued at $4,948.3 million in 2015, and it is anticipated to develop at a CAGR of 8.1% throughout the duration 2016 - 2022.The global market is increasing, due to growing food safety concern, developing demand in life science and scientific analysis sector, and growing healthcare expenditure and improvement of healthcare infrastructure. In addition, the technological developments with the advent of Mass Spectrometry equipment are in addition encouraging the boom of the market.
This report studies the global mass spectrometry market for the forecast duration of 2015 to 2020.This market is expected to reach USD 7,279.1 Million by 2020 from USD 4,919.9 in 2015 at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period.
Why Osaka, Japan?
Osaka is a designated city in the Kansai region of Japan. It is the capital city of Osaka Prefecture and the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, the second largest metropolitan area in Japan and among the largest in the world with over 19 million inhabitants. Osaka developed into a hub port connecting the region to the western part of Japan. The large numbers of increasingly larger tomb mounds found in the plains of Osaka are seen as evidence of political-power concentration, leading to the formation of a state. Osaka is a cosmopolitan city near the ancient capital, Kyoto, best known for its dynamic food and drinking culture, and famously outgoing people. It’s a surprisingly attractive and energetic city, with some of Japan’s most outgoing and fun-loving people, and world-class dining and drinking culture.
Related conference
- 3rd International Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics, May 20-21, 2019 Rome, Italy
- 8th World Congress on Mass Spectrometry, June 10-11, 2019 Edinburgh, Scotland
- International Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Chromatography, June 17-18, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- 8th International Conference on Advanced Mass Spectrometry & Chromatography, July 05-06, 2019 Columbus, USA
- 8th Congress on Analytical Chemistry & Mass Spectrometry, July 29-30, 2019 Bangkok, Thailand
- 9th International Conference and Exhibition on Spectroscopy and Analytical Techniques, Oct 17-18, 2019 Bangkok, Thailand
- 10th World Congress on Mass Spectrometry & Analytical Techniques, October 24-25, 2019 Prague, Czech Republic
- 10th Edition of International Conference on Mass Spectrometry, February 26-27, 2020 Dubai, UAE
Related Societies & Associations
USA Region
- American Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Brazilian Mass Spectrometry Society
- Canadian Society for Mass Spectrometry
- International Mass Spectrometry Foundation
- International Association of Forensic Toxicologists
- American Analytical Chemistry Laboratories Corporation
Europe Region
- British Mass Spectrometry Society
- Dutch Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Finnish Mass Spectrometry Society
- French Society for Mass Spectrometry
- German Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Irish Mass Spectrometry Society
- Italian Society of Mass Spectrometry
- Korean Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Norwegian Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Polish Mass Spectrometry Society
- Russian Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Spanish Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Swedish Mass Spectrometry Society
- Swiss Group for Mass Spectrometry
- Taiwan Society for Mass Spectrometry
- European Proteomics Association
- European Society for Separation Science
Asia Pacific Region
- China Mass Spectrometry Society
- Hong Kong Society of Mass Spectrometry
- Indian Society for Mass Spectrometry
- Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- Singapore Society for Mass Spectrometry
- South African Association for Mass Spectrometry
Conference Highlights
- Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry
- New Approaches & Recent Advancements in Mass Spectrometry
- Mass Spectrometry in Proteome Research
- Applications in Mass Spectrometry
- Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Maintenance, Troubleshooting, Data Analysis and Experimentation
- Ionization techniques
- Configurations and Separation Techniques
- Imaging Mass Spectrometry
- Mass Spectrometry in Food Analysis
- Mass Spectrometry in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis
- Mass Spectrometry of Polymers
- Mass Spectrometry in Environmental Analysis
- Mass Spectrometry in Forensic Science
- Mass Spectrometry in Drug Discovery and Drug Control
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | March 23-24, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journals of Bioprocessing & Biotechniques
- Journal of Analytical & Bioanalytical Techniques
- Journal of Chromatography & Separation Techniques
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by